Sweet potatoes are considered a low FODMAP food.
Although they do contain fructose, they contain more glucose, and that excess of glucose means that sweet potatoes are generally well tolerated even in those with IBS.
If that’s a little confusing to you, don’t worry. I’ll break down things as simply as possible in the rest of this post.
Table of Contents
FODMAP Breakdown of Sweet Potatoes
One research team analyzed the carbohydrate content of sweet potatoes.
They tested several varieties of sweet potato, so we can get a pretty detailed view of what the typical tuber contains in terms of sugars and starches.
Fructose in Sweet Potatoes
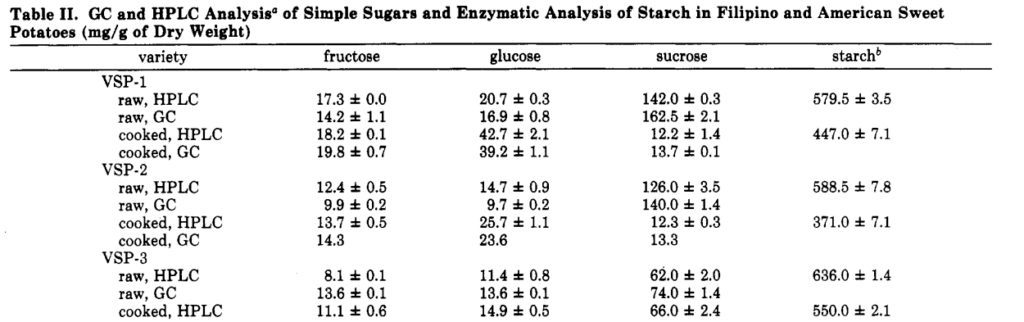
This first table below shows the main sugars fructose, glucose, and sucrose in both raw and cooked versions of different strains of potatoes:
It’s clear that sweet potatoes contain a significant amount of fructose, which is a FODMAP.
Values ranged from 11.1-19.8 mg of fructose per gram of cooked potato.
While that seems bad, it’s important to note that there was more glucose than fructose in every single sweet potato.
Research has shown that when there is as much or more glucose than fructose, the food is digested more easily.
Part of the definition of a high FODMAP food is:
FODMAPs are poorly absorbed short-chain carbohydrates including fructose (in excess of glucose)…
Let’s take a look at the remaining sugar breakdown from that original study before summing things up.
Sweet potatoes contain a significant amount of fructose, but more glucose. For most people, digesting glucose at the same time as fructose minimizes any digestive side effects.
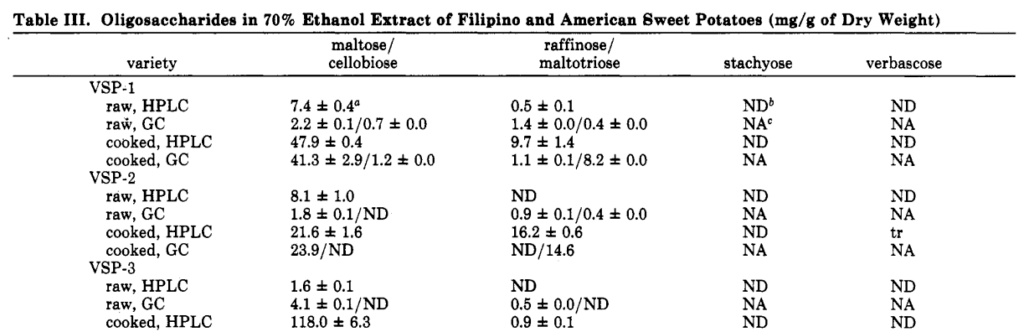
Oligosaccharides in Sweet Potatoes
The table below shows maltose, raffinose, stachyose, and verbascose. Note that maltose is not a FODMAP sugar.
The amount of raffinose is relatively small, but still significant.
Overall, it’s clear that while sweet potatoes do contain FODMAPs, they are relatively low in FODMAPs compared to other foods.
Are Sweet Potatoes OK for IBS?
Even though there are some FODMAPs, sweet potatoes typically don’t gas or other digestive issues. They’re usually okay to eat even if someone has IBS.
The fact that the levels of FODMAPs in sweet potatoes are reasonably low, plus that they have more glucose than fructose means that they are generally well tolerated.
Research on IBS usually includes sweet potato (along with all other types of potatoes) in their list of foods that are typically safe to eat (source):
The types of foods and beverages that are better tolerated include water; rice; plain pasta or noodles; baked or broiled potatoes; white breads; plain fish, chicken, turkey, or ham; eggs; dry cereals; soy or rice based products; peas; applesauce; cantaloupe; watermelon; fruit cocktail; margarine; jams; jellies; and peanut butter.
Not surprisingly, most of those foods are also low in FODMAPs (e.g. peanut butter is low FODMAP).
Other Factors Besides FODMAP Content That Affect Digestion
If you seem to have stomach issues after eating sweet potatoes, there are a few other potential explanations.
Baking or broiling sweet potatoes is recommended instead of frying them in a lot of oil, because large amounts of oil can cause additional stomach problems.
Finally, remember that quantity matters. For most people, eating a small sweet potato won’t cause digestion troubles, but eating a much larger serving might. You’ll need to test your limits to establish where you might have to draw the line.